The tall glass columns which are packed with a synthetic ion-exchange resin is used to carry out the separation. (Resins are the polymers to which various ionizable groups have been chemically added).
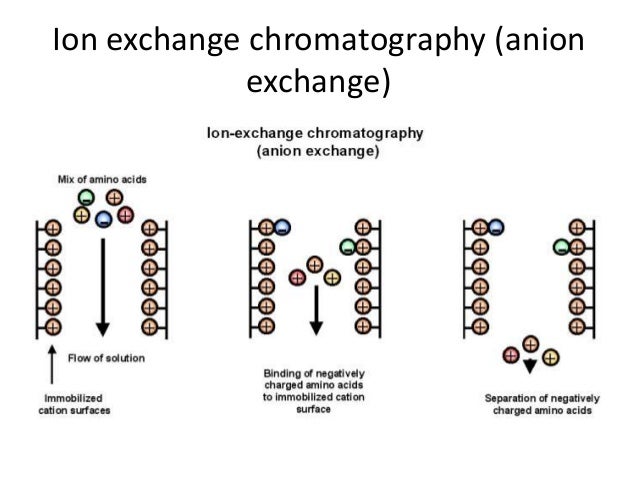 |
| Example of anion exchange. |
Resins which have negative charges are called cation exchangers and those which have positive charges are called anion exchangers. When the solution of ions are passed through the column, the ions compete with each other for the charged sites on the resin. The rate of movement of any ion through the column depends on its affinity for the resin sites, its degree of ionization and the nature and concentration of competing ions in the solution.
Molecules such as proteins and nucleic acids posses a variety of positively and negatively charged groups. For their separations, the differential rates of movement of ions through the column are basis for them.
Some of anion exchangers are Dowex-2, Bio-Rad AG2, QAESephadex, Diethylam noethylcellulose.
Some of cation exchangers are caboxymethylkellulose, BioRad AG50, Zeocarb 225. Amberlite IRC50.
Comments
Post a Comment