The method of separation of cells from tissue or separation of cell sub populations from a heterogeneous population of cells is called cell sorting. Cell separation is commonly achieved by separating them based on cell size and cell shape, cell density, granularity and bio-marker expression or protein marker expression. There are various methods for cell sorting such as Density Gradient Centrifugation, Filtration, Aptamer binding, plastic/adhesion, LCM, RCB rosetting, FACS and MACS. Commonly used are Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) and Magnetic Activated Cell Sorting (MACS).
Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorting can be defined as the physical separation of sub populations of cells based on the protein expression markers which are tagged with fluorescence molecules, and subsequent collection of these sub populations in a media or buffer. Cell sorting using this method has many applications such as establishing a stable lines, enriching cell populations of interest, proteome and genome studies, disease monitoring, etc. Sorting in a flow cytometer is more complex than only analysis part. However, the sorted sub populations of cells have more applications in down stream experiments and cell culturing.
Principle: "A single cell suspension of cells are tagged with fluorescent molecules are passed through a sheath fluid so that cells align in a single file fashion and cells passed through a nozzle one at time. Due to vibrating mechanism, the nozzle vibrates at about 40,000 to 50,000 cycles per second and breaks the stream into 40,000 to 50,000 droplets per second. These droplets may contain the target cell. The laser beam is directed at the stream just before the stream breaks up into droplets. If the cell meets the criteria of having fluorescence and size, an electrical charge (positive or negative) is given to the stream. As the charged droplets pass between a a pair of electrical plates, negatively charged drops are attracted towards the positively charges plate and vice versa. The uncharged drops pass into a waste container."
"Flow cytometers are analyzers and cell sorters. But, All Analyzers are not Cell Sorters".
"A good sample preparation will lead to a good sorting experiment".
FASC has various system components which work together to achieve successful sorting of cell sub populations. Main Components are Fluidics, Optics, Sorting Systems, Sort Collection.
Cell suspension is introduced through a sample injection port to the flow cell, where with help of sheath fluid and hydrodynamic focusing, cells will align in a single file fashion, allowing the cells to pass through nozzle one by one. A piezoelectric device is installed in the flow cell which vibrates the nozzle in acoustic wave forming droplets at a specified frequency. Once the target cell is detected,the stream charging wire will charge the droplets which contain the target cells.
Drop Delay can defined as the distance between laser interrogation point and drop break-off point. Drop delay determines how long system should wait before it applies charge once the target is detected.
Drop delay should be accurate for cell sorting experiments.
Once the target particle or cell is detected, the droplets containing the targets cells will be given charge (either positive or negative charge) after proper drop delay. These charged droplets travel between two electrical charge plates (Positive Plate and negative plate). These plates will attract the opposite charged droplets and these attracted droplets are then collected into a collection buffer. (Positive Charge Plate will attract the negatively charged droplets containing target cell).
"How Two-Way Cell Sorting Works?" (Practical)
Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorting can be defined as the physical separation of sub populations of cells based on the protein expression markers which are tagged with fluorescence molecules, and subsequent collection of these sub populations in a media or buffer. Cell sorting using this method has many applications such as establishing a stable lines, enriching cell populations of interest, proteome and genome studies, disease monitoring, etc. Sorting in a flow cytometer is more complex than only analysis part. However, the sorted sub populations of cells have more applications in down stream experiments and cell culturing.
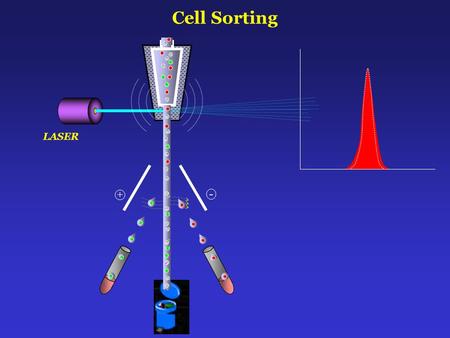 |
| Source: Cell Sorting + - LASER Zhang at al, Blood Slideshare |
Principle: "A single cell suspension of cells are tagged with fluorescent molecules are passed through a sheath fluid so that cells align in a single file fashion and cells passed through a nozzle one at time. Due to vibrating mechanism, the nozzle vibrates at about 40,000 to 50,000 cycles per second and breaks the stream into 40,000 to 50,000 droplets per second. These droplets may contain the target cell. The laser beam is directed at the stream just before the stream breaks up into droplets. If the cell meets the criteria of having fluorescence and size, an electrical charge (positive or negative) is given to the stream. As the charged droplets pass between a a pair of electrical plates, negatively charged drops are attracted towards the positively charges plate and vice versa. The uncharged drops pass into a waste container."
"Flow cytometers are analyzers and cell sorters. But, All Analyzers are not Cell Sorters".
"A good sample preparation will lead to a good sorting experiment".
FASC has various system components which work together to achieve successful sorting of cell sub populations. Main Components are Fluidics, Optics, Sorting Systems, Sort Collection.
Cell suspension is introduced through a sample injection port to the flow cell, where with help of sheath fluid and hydrodynamic focusing, cells will align in a single file fashion, allowing the cells to pass through nozzle one by one. A piezoelectric device is installed in the flow cell which vibrates the nozzle in acoustic wave forming droplets at a specified frequency. Once the target cell is detected,the stream charging wire will charge the droplets which contain the target cells.
Drop Delay can defined as the distance between laser interrogation point and drop break-off point. Drop delay determines how long system should wait before it applies charge once the target is detected.
Drop delay should be accurate for cell sorting experiments.
Once the target particle or cell is detected, the droplets containing the targets cells will be given charge (either positive or negative charge) after proper drop delay. These charged droplets travel between two electrical charge plates (Positive Plate and negative plate). These plates will attract the opposite charged droplets and these attracted droplets are then collected into a collection buffer. (Positive Charge Plate will attract the negatively charged droplets containing target cell).
"How Two-Way Cell Sorting Works?" (Practical)
Comments
Post a Comment