A microscope that uses fluorescence to magnify or produce an image is referred to as fluorescence microscope. Fluorescence microscopes can be epifluorescence microscope (A simple set up) or confocal microscope (a complex microscope which is installed with optical sectioning to produce an image with a better resolution). They wide range of applications in investigating organic or inorganic substances.
 |
| Image Source: /serc.carleton.edu |
"A fluorescence molecule is excited at a specific wavelength will emit the light wavelength with lower energy and longer wavelength than that of the excited wavelength".
"Fluorescence Microscopy involves the investigating the extra or intra cellular molecules such as proteins, surface markers which are tagged with specific fluorescence molecules.
Epifluorescence microscopes are widely used in biological sciences and these scopes are basis for the advanced complex fluorescence microscopes such as confocal microscopes.
Components of a typical fluorescence microscope are light source (xenon arc lamp or lasers), excitation and emission filters, dichroic mirrors.
Principle of Fluorescence Microscopy:
"The light of specific wavelength is used to illuminate the specimen. The fluorophores present inside the specimen will absorb this wavelength of light which in turn emits the light at longer wavelength (different color than absorbed). The emitted light will have lower energy than the absorbed light. Then specific emission filters and dichroic mirrors are used to match the excitation and emission wavelengths of the fluorophore which is used to study the specimen. In this manner, single fluorophore distribution inside the specimen is magnified and image is produced".
How Fluorescence Microscopy Works?:
 Light source such as xenon arc lamp or laser will give a light wavelength with higher energy which travels through a excitation filter. Excitation filter makes sure that specific wavelength of light is passed to excite the fluorophore whose excitation matches. filtered light then travels through the dichroic mirror which in turn reflects the light at 90 degree. The reflected light passes through the objective lens to the specimen. Then specimen will emit the light with longer wavelength and lower energy.. This emitted light is filtered using emission filter placed just before the detector. The detector will then capture this emitted light which in turn can be observed through eye piece or specialized camera which produces fluorescing images on a computer.
Light source such as xenon arc lamp or laser will give a light wavelength with higher energy which travels through a excitation filter. Excitation filter makes sure that specific wavelength of light is passed to excite the fluorophore whose excitation matches. filtered light then travels through the dichroic mirror which in turn reflects the light at 90 degree. The reflected light passes through the objective lens to the specimen. Then specimen will emit the light with longer wavelength and lower energy.. This emitted light is filtered using emission filter placed just before the detector. The detector will then capture this emitted light which in turn can be observed through eye piece or specialized camera which produces fluorescing images on a computer.
Most commonly used microscopes are epi-fluorescence microscopes where excitation of the fluorophore and detection of the emitted fluorescence are done through the same path, that is through the objective lens.
Sample preparation involves the staining the cells with fluorescent molecules. For fluorescence microscopy, the specimen must be fluorescent. Expressing the fluorescent proteins.
In immunofluorescence, the specific antibody is directly conjugated with a fluorophore. this fluorescent-conjugated antibody binds specifically to an antigen. (Here, secondary antibody can also be used).
Example Images:
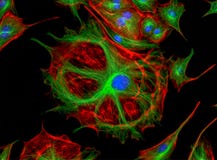

Applications:
* Imaging structural components of small objects, such as cells or micro organisms.
* Investigating viability tests on cell populations (involves the live or dead staining).
* Imaging genetic material within the cells (DNA or RNA)
* Imaging the specific cell types within a heterogeneous populations of cells.
Comments
Post a Comment