Please Watch The Demo Video attached after the protocol and example Data!!!!
1) Suspend approximately million cells (10^6) in 1mL of 1x PBS (phosphate-buffered saline solution). and with the help of pipette, gently aspirate (up and down) about 7-8 times, to make the single cell suspension.
2) Take a centrifuge tube and add 4mL of 70% ethanol.. (70% ethanol should be in ice before using). and add 1mL of cells in PBS to the same tube. Keep the tubes on ice for minimum 2 hours. This step is to fix the cells. (Cells can be kept at 4℃ for a week).
3) Centrifuge the ethanol fixed cells for 5 minutes at 300g. Carefully take out the supernatant. Do not disturb the pellet.
4) Add 5mL of cold 1xPBS to this pellet and suspend the cells using pipette.
5) Centrifuge the tubes at 300g for 5 minutes. Discard the supernatant. Again do not disturb the pellet.
6) If required, step 5 can be repeated for one more time.
7) Add 1mL of Propidium Iodide (PI) solution to the pellet and suspend the pellet using pipette. (PI concentration should be 50µg/mL. (Additionally you can add 100µg/mL RNase A before adding PI to degrade the RNA if present in the sample).
8) Keep the tubes at room temperature for at least 30 minutes in the dark. (Note: You can keep the tubes at 37℃ for 10 minutes to speed up things).
9) Trasnfer PI stained cells to flow cytometer tubes and run the samples on flow cytometer for the cell cycle analysis as soon as possible. (if there are clumps in the sample, vortex them or pipette them up and down until there are no clumps before running the samples tubes on flow cytometer).
10) For excitation of PI, 488nm or 561nm lasers can be used and emission at 620nm.
Other Notes:
1) Be sure to use approximately equal number of cells in each tubes. better to count the cells before proceeding using hematocytometer.
2) Try to get a good single cell suspension for better staining and better cell cycle analysis.
3) Use proper and equal PI concentration for each sample tubes.
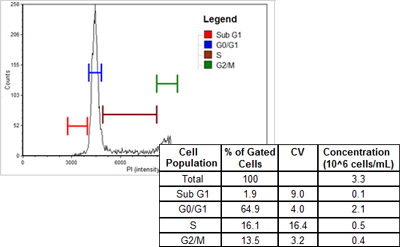
Please Watch The Demo Video attached below on How You Can Analyze Cell Cycle in a Flow Cytometer and What to Gate and Consider
 |
| Source: Nexcelom Bioscience |
Comments
Post a Comment